TiKV 是一个分布式事务型的键值数据库,是TiDB的存储层,提供了满足 ACID 约束的分布式事务接口,并且通过 Raft 协议保证了多副本数据一致性以及高可用。关于TiDB、TiKV的详细介绍可以从官网查阅,这里就不多赘述了。
知乎上已经有一篇高屋建瓴的文章,由Ed写的TiKV代码初探,可以从整体了解TiKV的内部功能,不过作为喜欢阅读代码的攻城狮来说,更喜欢来一个庖丁解牛式的分析。所以我们从代码级别粗略的分析一下TiKV。
TiKV 源码初探
概述本文档主要面向 TiKV 社区开发者,主要介绍 TiKV 的系统架构,源码结构,流程解析。目的是使得开发者阅读文档之后,能对 TiKV 项目有一个初步了解,更好的参与进入 TiKV 的开发中。 需要注意,TiKV 使用 Rust …
我们首先选择了Config这部分代码逻辑来分析,一个是相对其他功能模块来说,这部分代码没有太烧脑的算法逻辑,另一个原因是这部分代码是整个TiKV启动后马上运行的部分,是最先碰到的代码逻辑,再有就是可以通过配置代码大体了解TiKV内部那些重要的功能模块们,从而避免繁杂的细节导致窥测一斑的局限。如果想整体了解配置字段,我们可以从官网上查阅完整的配置说明文档。
文章中所参考的代码是基于Oct 29, 2020 master分支来进行分析的,可能会和最新的代码有出入,读者需要按照实际情况判别。
从配置流程主干流程上可以看到,系统从cmd/bin/tikv-server开始运行,进入cmd/src/setup获取配置文件参数,之后进入src/config.rs执行各个模块的配置逻辑。
Setup Config Main Flow
src/config.rs内以TiKvConfig struct为起始点,从外部读取配置信息后完成配置初始化工作,以下是TiKvConfig内部的字段。
| Fields | Sub-Fields | Type | Cmd Args |
|---|---|---|---|
| cfg_path | String | ||
| log_level | slog::Level | log-level | |
| log_file | String | log-file | |
| log_format | LogFormat | ||
| slow_log_file | String | ||
| slow_log_threshold | ReadableDuration | ||
| log_rotation_timespan | ReadableDuration | ||
| log_rotation_size | ReadableSize | ||
| panic_when_unexpected_key_or_data | bool | ||
| readpool | ReadPoolConfig | ||
| server | - | ServerConfig | |
| addr | addr | ||
| advertise_addr | advertise-addr | ||
| status_addr | status-addr | ||
| advertise_status_addr | advertise-status-addr | ||
| labels | |||
| storage | - | StorageConfig | |
| data_dir | data-dir | ||
| pd | - | PdConfig | |
| endpoints | pd-endpoints | ||
| metric | - | MetricConfig | |
| address | metrics-addr | ||
| raft_store | - | RaftStoreConfig | |
| capacity | capacity | ||
| coprocessor | CopConfig | ||
| rocksdb | DbConfig | ||
| raft_engine | RaftEngineConfig | ||
| security | SecurityConfig | ||
| import | ImportConfig | ||
| backup | BackupConfig | ||
| pessimistic_txn | PessimisticTxnConfig | ||
| gc | GcConfig | ||
| split | SplitConfig | ||
| cdc | cdcConfig |
所以我们下面按照代码顺序,依次介绍每个模块的作用和配置检查逻辑所做的事情,流程图内镂空的图例是每个流程图的起始点。
readpool
这是一个独立的用于数据读取的线程池,主要解决单一线程池导致的读写性能阻塞问题,具体的设计细节可以查看Read Pool RFC。
readpool内的unifed read pool还处于试验阶段,其他两个config都是通过readpool_config宏来定义的,所以他们的逻辑都是一样的,针对并发配置做了检查。
storage
从名字上就能看出这块代码主要负责存储相关的内容,打开项目代码,可以看出不光包含kv数据落盘的逻辑,还包括mvcc,txn一系列相关操作。validate部分比较简单,就是对数据存储的目录进行检查和校验,另外对4.0版本之后的优化配置也进行了检测。
src/storage/config.rs, Config struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| data_dir | String | “./” |
| gc_ratio_threshold | f64 | 1.1 |
| max_key_size | usize | 4 * 1024 |
| scheduler_concurrency | usize | 1024 * 512 |
| scheduler_worker_pool_size | usize | if cpu_num >= 16.0 { 8 } else { 4 } |
| scheduler_pending_write_threshold | ReadableSize | 100MB |
| reserve_space | ReadableSize | 2 |
| enable_async_commit | bool | true |
| block_cache | BlockCacheConfig | BlockCacheConfig::default() |
paths and grpc
这部分配置逻辑没有独立成一个validate方法,我们作为一个整体看一下主要做了哪几件事情:
- 设置region拆分检查的大小=6MB
- 配置config目录,当空时配置cfg_path为storage.data_dir,默认配置下为"./"
- 配置raftdb目录,当空时配置为storage.data_dir"/raft",默认配置下为"./raft"
- 配置raft-engine目录,当空时配置为storage.data_dir"/raft-engine",默认配置下为"./raft-engine"
- 配置rocksdb目录,默认配置为storage.dat_dir"/db",也就是"./db"。但是这个路径不能和raftdb放在一起,所以会有一个检查,检查有问题会抛出"raft_store.raftdb_path can not same with storage.data_dir/db"的错误。之后会根据kv_db_path, raft_store.raftdb_path, raft_engine.config.dir对目录内的数据库文件进行检查,判断是否存在对应的数据库。
rocksdb
从变量名字上可以知道,这部分的代码逻辑是配置核心数据库的,也就是rocksdb的配置。我们可以看到这里主要是对cf做检测,cf的命名猜测应该是column family的简称,而主要检查内容就是块大小不能大于32MB。另外还有对titan和rocksdb的unordered_write配置检查。titan是PingCAP开发的一个用来减少写放大问题的rocksdb插件,titan的理论基础来自于WiscKey。而unorder_write是一个提高rocksdb写性能的配置。这里有几篇文章可以扩展阅读一下。
RocksDB Config
How TiKV reads and writes
Tune TiKV Performance
Titan Config
WiscKey: Separating Keys from Values in SSD-conscious Storage
Higher write throughput with unordered_write feature
src/config.rs, DbConfig struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| info_log_level | LogLevel | LogLevel::Info |
| wal_recovery_mode | DBRecoveryMode | DBRecoveryMode::PointInTime |
| wal_dir | String | “” |
| wal_ttl_seconds | u64 | 0 |
| wal_size_limit | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(0) |
| max_total_wal_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::gb(4) |
| max_background_jobs | i32 | 8 |
| max_manifest_file_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(128) |
| create_if_missing | bool | true |
| max_open_files | i32 | 40960 |
| enable_statistics | bool | true |
| stats_dump_period | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| compaction_readahead_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(0) |
| info_log_max_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::gb(1) |
| info_log_roll_time | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(0) |
| info_log_keep_log_file_num | u64 | 10 |
| info_log_dir | String | “” |
| rate_bytes_per_sec | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(0) |
| rate_limiter_refill_period | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(100) |
| rate_limiter_mode | DBRateLimiterMode | DBRateLimiterMode::WriteOnly |
| auto_tuned | bool | false |
| bytes_per_sync | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(1) |
| max_sub_compactions | u32 | 3 |
| writeable_file_max_buffer_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(1) |
| use_direct_io_for_flush_and_compaction | bool | false |
| enable_pipelined_write | bool | true |
| enable_multi_batch_write | bool | true |
| enable_unordered_write | bool | false |
| defaultcf | DefaultCfConfig | DefaultCfConfig::default() |
| writecf | WriteCfConfig | WriteCfConfig::default() |
| lockcf | LockCfConfig | LockCfConfig::default() |
| raftcf | RaftCfConfig | RaftCfConfig::default() |
| ver_defaultcf | VersionCfConfig | VersionCfConfig::default() |
| titan | TitanDBConfig | TitanDBConfig::default() |
| titan.max_background_gc | max_background_gc |
raftdb
每一个TiKV都包含两个rocksdb实例,一个是用来存储真实数据的我们称之为kv rocksdb,就是我们上面介绍的rocksdb变量对应的配置;另一个用来存储raft log,我们称之为raft rocksdb,也就是这个raftdb变量对应的配置,用来存放multi-raft log的数据。可以参考下面的文章进行配置和调优工作。
Raftstore Config
Tune TiKV Performance
src/config.rs, RaftDbConfig struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| wal_recovery_mode | DBRecoveryMode | DBRecoveryMode::PointInTime |
| wal_dir | String | “” |
| wal_ttl_seconds | u64 | 0 |
| wal_size_limit | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(0) |
| max_total_wal_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::gb(4) |
| max_background_jobs | i32 | 4 |
| max_manifest_file_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(20) |
| create_if_missing | bool | true |
| max_open_files | i32 | 40960 |
| enable_statistics | bool | true |
| stats_dump_period | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| compaction_readahead_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(0) |
| info_log_max_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::gb(1) |
| info_log_roll_time | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(0) |
| info_log_keep_log_file_num | u64 | 10 |
| info_log_dir | String | “” |
| info_log_level | LogLevel | LogLevel::Info |
| max_sub_compactions | u32 | 2 |
| writable_file_max_buffer_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(1) |
| use_direct_io_for_flush_and_compaction | bool | false |
| enable_pipelined_write | bool | true |
| enable_unordered_write | bool | false |
| allow_concurrent_memtable_write | bool | true |
| bytes_per_sync | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(1) |
| wal_bytes_per_sync | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::kb(512) |
| defaultcf | RaftDefaultCfConfig | RaftDefaultCfConfig::default() |
| titan | TitanDBConfig | TitanDBConfig::default() |
| titan.max_backgound_gc | 4 |
raft_engine
raft engine应用了另一个tikv的git库,所对应的validate逻辑也不复杂,就检验了purge阈值。但从raft engine的readme看,这是一个存放multi-raft log的数据引擎,用来解决raftdb出现的性能问题,最终会替换raftdb。从文中声称的性能测试结果来看,确实有非常大的提升。
server
从流程图上也可以看出,服务器配置相对来说是所有配置里面算逻辑复杂的,但大体上分成几个部分:对ip地址/端口的检查,snapshot收发量检查,被调用的递归深度和时长的检查,grpc的配置检查。
src/server/config.rs, Config struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| cluster_id | u64 | 0 |
| addr | String | “127.0.0.1:20160” |
| advertise_addr | String | “” |
| status_addr | String | “127.0.0.1:20180” |
| advertise_status_addr | String | “” |
| status_thread_pool_size | usize | 1 |
| max_grpc_send_msg_len | i32 | 10 * 1024 * 1024 |
| grpc_compression_type | GrpcCompressionType | GrpcCompressionType::None |
| grpc_concurrency | usize | 4 |
| grpc_concurrent_stream | i32 | 1024 |
| grpc_raft_conn_num | usize | 1 |
| grpc_memory_pool_quota | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(2 * 1024 * 1024) |
| grpc_stream_initial_window_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(isize::MAX) |
| grpc_keepalive_time | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| grpc_keepalive_timeout | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(3) |
| concurrent_send_snap_limit | usize | 32 |
| concurrent_recv_snap_limit | usize | 32 |
| end_point_recursion_limit | u32 | 1000 |
| end_point_stream_channel_size | usize | 8 |
| end_point_batch_row_limit | usize | 64 |
| end_point_stream_batch_row_limit | usize | 128 |
| end_point_enable_batch_if_possible | bool | true |
| end_point_request_max_handle_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(60) |
| end_point_max_concurrency | usize | cmp::max(cpu_num, 4) |
| end_point_check_memory_locks | bool | true |
| snap_max_write_bytes_per_sec | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(100 * 1024 * 1024) |
| snap_max_total_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(0) |
| stats_concurrency | usize | 1 |
| heavy_load_threshold | usize | 300 |
| heavy_load_wait_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(1) |
| enable_request_batch | bool | true |
| labels | HashMap<String, String> | HashMap::default() |
| raft_client_backoff_step // Test only. | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(1) |
raft_store
这个是所有配置逻辑里面最复杂的部分了,不过主要还是围绕raft算法进行配置,包括:Leader选举(Leader election)、日志同步(Log replication)、安全性(Safety)、日志压缩(Log compaction)、成员变更(Membership change)等。到此我们其实看到有三处地方与raft配置有关系的代码,设置raft存储目录,raftdb配置,raftstore配置,是不是可以把这些代码放在一起来维护?
以下是对于raft store逻辑的扩展阅读:
Raftstore Config
关于raft算法这里就不详细讲解了,需要深入了解的同学可以参考这篇知乎。
Raft算法详解
当然pingcap在raft paper的基础上做了很多优化措施,具体细节可以参考这篇文章。
TiKV 功能介绍 - Raft 的优化
component/raftstore/src/store/config.rs, Config struct
let split_size = ReadableSize::mb(coprocessor::config::SPLIT_SIZE_MB) // SPLIT_SIZE_MB=96
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| prevote | bool | true |
| raftdb_path | String | String::new() |
| capacity | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(0) |
| raft_base_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(1) |
| raft_heartbeat_ticks | usize | 2 |
| raft_election_timeout_ticks | usize | 10 |
| raft_min_election_timeout_ticks | usize | 0 |
| raft_max_election_timeout_ticks | usize | 0 |
| raft_max_size_per_msg | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(1) |
| raft_max_inflight_msgs | usize | 256 |
| raft_entry_max_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(8) |
| raft_log_gc_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| raft_log_gc_threshold | u64 | 50 |
| raft_log_gc_count_limit | u64 | split_size * 3 / 4 / ReadableSize::kb(1) |
| raft_log_gc_size_limit | ReadableSize | split_size * 3 / 4 |
| raft_log_reserve_max_ticks | usize | 6 |
| raft_engine_purge_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| raft_entry_cache_life_time | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(30) |
| raft_reject_transfer_leader_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(3) |
| split_region_check_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| region_split_check_diff | ReadableDuration | split_size / 16 |
| region_compact_check_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(5) |
| region_compact_check_step | u64 | 100 |
| region_compact_min_tombstones | u64 | 10000 |
| region_compact_tombstones_percent | u64 | 30 |
| pd_heartbeat_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(1) |
| pd_store_heartbeat_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| snap_mgr_gc_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(1) |
| snap_gc_timeout | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::hours(4) |
| lock_cf_compact_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| lock_cf_compact_bytes_threshold | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(256) |
| notify_capacity | usize | 40960 |
| messages_per_tick | usize | 4096 |
| max_peer_down_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(5) |
| max_leader_missing_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::hours(2) |
| abnormal_leader_missing_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| peer_stale_state_check_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(5) |
| leader_transfer_max_log_lag | u64 | 10 |
| snap_apply_batch_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize::mb(10) |
| consistency_check_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| report_region_flow_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(1) |
| raft_store_max_leader_lease | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(9) |
| right_derive_when_split | bool | true |
| allow_remove_leader | bool | false |
| merge_max_log_gap | u64 | 10 |
| merge_check_tick_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::secs(10) |
| use_delete_range | bool | false |
| cleanup_import_sst_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| local_read_batch_size | u64 | 1024 |
| apply_batch_system | BatchSystemConfig | BatchSystemConfig::default() |
| store_batch_system | BatchSystemConfig | BatchSystemConfig::default() |
| future_poll_size | usize | 1 |
| hibernate_regions | bool | true |
| hibernate_timeout | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
| early_apply | bool | true |
| dev_assert | bool | false |
| apply_yield_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(500) |
| region_max_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(0) |
| region_split_size | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(0) |
| clean_stale_peer_delay | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(0) |
| perf_level | PerfLevel | PerfLevel::Disable |
pd
pd是placement driver的缩写,用来管理整个tikv集群,是整个集群的中央控制器,负责整个集群的调度工作。tikv内是pd client的逻辑,所以对配置的检查逻辑相对比较简单。
component/pd_client/src/config.rs, Config struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| endpoints | Vec | vec![“127.0.0.1:2379”.to_string()] |
| retry_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(300) |
| retry_max_count | isize | std::isize::MAX |
| retry_log_every | usize | 10 |
| update_interval | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
coprocessor
类似于Hbase,tikv提供了一个协处理器框架来支持分布式计算。主要的功能是,每个节点在接收到分布式请求处理之后把自己负责的数据先做一次处理。这里不仅能提高整体运算效率,还能有效减少网络开销。需要具体了解coprocessor,可以参考这篇文章。
TiKV 源码解析系列文章(十四)Coprocessor 概览
components/raftstore/src/coprocessor/config.rs, Config struct
let split_size = ReadableSize::mb(96);
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| split_region_on_table | bool | false |
| batch_split_limit | u64 | 10 |
| region_max_size | ReadableSize | split_size |
| region_split_size | ReadableSize | split_size / 2 * 3 |
| region_max_keys | u64 | 960000 / 2 * 3 |
| region_split_keys | u64 | 960000 |
| consistency_check_method | ConsistencyCheckMethod | ConsistencyCheckMethod::Raw |
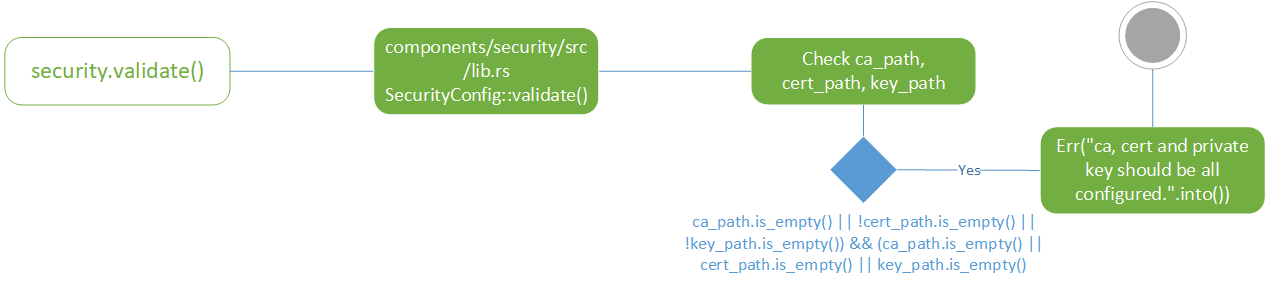
security
security一看就知道是负责安全相关的逻辑,validate代码里主要检查了证书,密钥等一系列配置。security的config struct和其他模块不太一样,居然放在lib.rs里面,是不是可以考虑移出来,跟其他模块保持一致呢?
components/security/src/lib.rs, SecurityConfig struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| ca_path | String | String::new() |
| cert_path | String | String::new() |
| key_path | String | String::new() |
| override_ssl_target | String | String::new() |
| cert_allowed_cn | HashSet | HashSet::default() |
| redact_info_log | Option | None |
| encryption | EncryptionConfig | EncryptionConfig::default() |
import
这里的import老实说没有能从代码引用关系找到对应代码文件,当然在浏览全项目文件之后找到了一个有近似逻辑的文件,所以这部分之后还需要跟tikv团队确认一下。
import的主要功能是磁盘加载rocksdb的文件,在代码中会看到sst这样的缩写,sst其实是rocksdb生成的文件格式名称,但由于不同的应用场景,这种文件格式其实有好几种结构:block-based table, plain table, cuckoo table和index block。
block-based table是sst文件的默认格式结构,这种格式下默认block大小为4kb,所有存储在文件内的key都是被排序过的,所以利用二叉搜索算法能够快速搜索到对应的键值。具体block-based table详解和其他格式结构可以参考一下文章:
| SST File Formats | Links |
|---|---|
| Rocksdb BlockBasedTable Format | https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb/wiki/Rocksdb-BlockBasedTable-Format |
| PlainTable Format | https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb/wiki/PlainTable-Format |
| CuckooTable Format | https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb/wiki/CuckooTable-Format |
| Index Block Format | https://github.com/facebook/roc |
validate检查的内容也很简单,就是threads和window两个变量。
components/sst_importer/src/config.rs, Config struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| num_threads | usize | 8 |
| stream_channel_window | usize | 128 |
| import_mode_timeout | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::minutes(10) |
backup
这部份应该是关于数据备份相关的配置代码,里面其实就一个字段num_threads,默认最多75%cpu来做备份的工作。
pessimistic_txn
从名字上看,这是一个悲观锁事务的配置验证。悲观锁和乐观锁的概念是大学数据库课程的基本概念,这里可以看一下tikv的解释说明,这篇文章也指出tikv主要使用乐观锁,所以这里的配置检查只是保证在使用悲观锁时的锁定时长不能等于0毫秒。
Locking
src/server/lock_manager/config.rs, Config struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| wait_for_lock_timeout | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(1000) |
| wake_up_delay_duration | ReadableDuration | ReadableDuration::millis(20) |
| piplelined | bool | false |
gc
这部分代码应该是检查垃圾回收配置的逻辑,关于垃圾回收的官方文档目前只有在2.1版本里能找到,不过在用户文档里有相关的内容。
gc的任务也比较清楚,就是清理不再需要的旧数据。这里检查的batch_keys会在src/server/gc_worker/gc_worker.rs内被用来设定批量扫描的范围,所以这个值肯定不能等于0。
// Scans at most `GcConfig.batch_keys` keys.
let (keys, updated_next_key) = reader.scan_keys(next_key, self.cfg.batch_keys)?;
src/server/gc_worker/config.rs, GcConfig struct
| Fields | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| ratio_threshold | f64 | 1.1 |
| batch_keys | usize | 512 |
| max_write_bytes_per_sec | ReadableSize | ReadableSize(0) |
| enable_compaction_filter | bool | false |
| compaction_filter_skip_version_check | bool | false |
最后贴上完整的config流程图,图有点大,只能看个大概。